
Gartner recently published the 2022 Magic Quadrant for Managed Network Services (MNS) which identified ATSG Optanix as a Leader for MNS. This is the first time that the company has been named a Leader in the Magic Quadrant, after two consecutive years as a Challenger.
Placement in the MNS Magic Quadrant is based on Gartner analysts’ evaluation of ATSG Optanix’s ability to execute and its completeness of vision among the vendors in the MNS market.
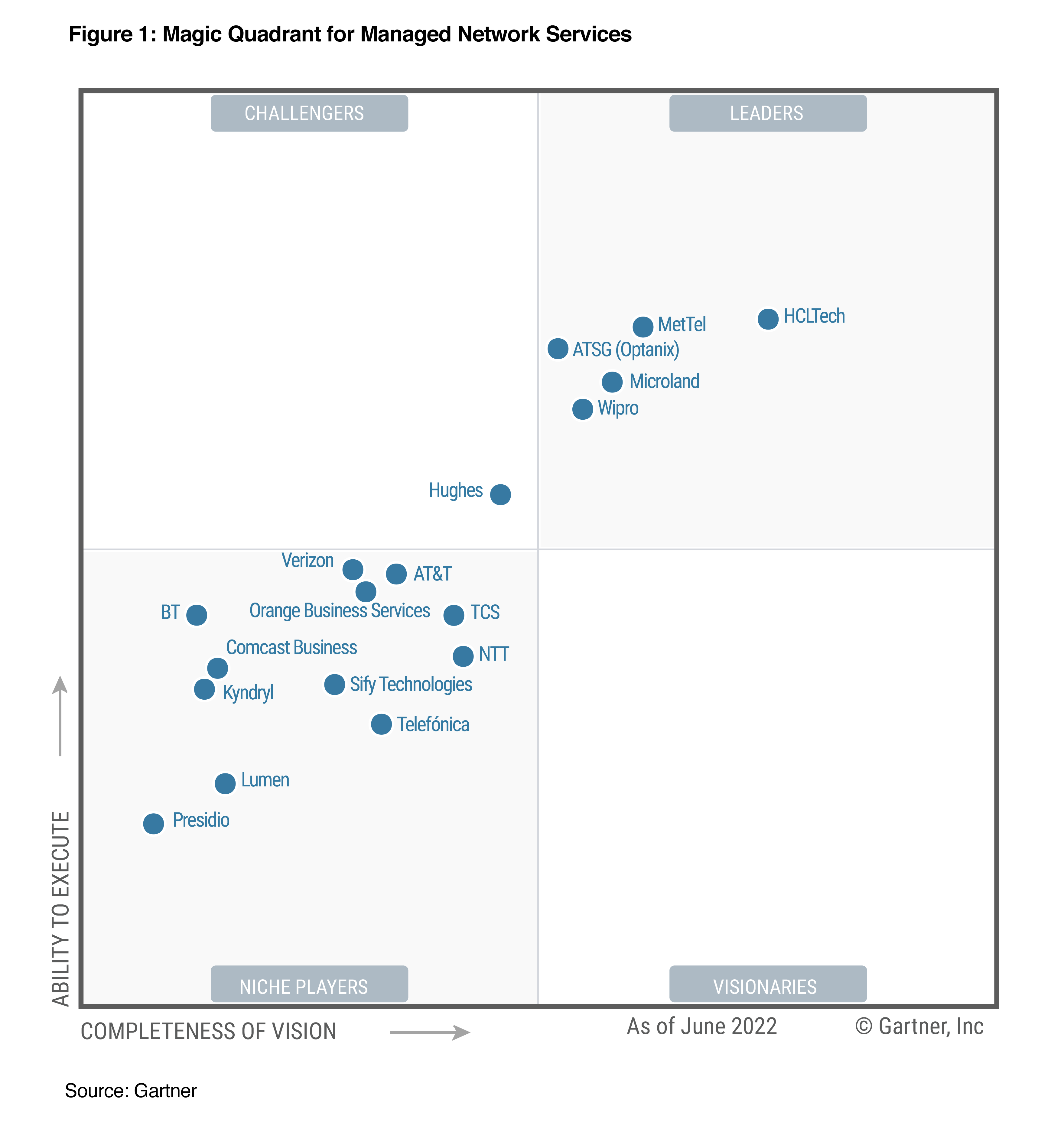
Evaluation of ATSG Optanix’s Managed Network Services by Gartner
According to Gartner, “a provider in the Leaders quadrant demonstrates the ability to fulfill a broad variety of customer requirements through the breadth of its MNS offerings. Leaders have the ability to shape the market and provide complete and differentiating services, as well as global service and support Leaders maintain strong relationships with their channels and customers, and have no obvious gaps in their portfolios.”
“One of the evaluation criteria is Market Responsiveness/Record which talks about Ability to respond, change direction, be flexible and achieve competitive success as opportunities develop, competitors act, customer needs evolve and market dynamics change. This criterion also considers the vendor’s history of responsiveness.”
Gartner estimates that by the end of 2024, 35% of enterprise buyers will demand MNS services to include near-real-time case management and consistently maintained data repository (CMDB) synchronization with enterprise IT service management (ITSM) tools.
We believe ATSG Optanix’s MNS offering takes an integrated organizational approach that combines people, processes and technology into a comprehensive service assurance solution. It occupies a unique space in the market as a longtime managed service provider with its own internally developed full-stack service assurance platform and global delivery model, providing customers with real-time dashboards and ITSM integrations.
ATSG Optanix Managed Network Services Differentiators
ATSG Optanix believes that by combining our accredited staff, client focused processes, and internal AIOps technology investments in a consolidated solution, ATSG Optanix operationalizes managed services extremely quickly. Our deployment time can be measured in weeks, not quarters. This approach makes ATSG Optanix a nimble provider that enterprises can strategically engage to manage WAN, LAN, Unified Communications and Contact Center.
We provide customers with a continuum of visibility that makes our managed services offering totally transparent. We call this approach our “Service Vernacular” deployment method, where we match the WAN/LAN services delivered to how the customer I&O leaders support the internal business units of their enterprise. This suite includes:
- Live and real-time portal access of monitoring and telemetry data by which we share information at the engineering level. This allows our customers to see what our engineers see in their environment
- The ability to align our operations with what matters most to a customer’s business. We do this with business impact monitoring models and real-time dashboards curated for the customer.
- An accountability dimension enabled via e-bonding, by which we open our tickets up to the customer so that they can observe our activity firsthand, and measure it themselves through their own ITSM investments.
GARTNER and Magic Quadrant are registered trademarks and service marks of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and internationally and are used herein with permission. All rights reserved.
Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in its research publications, and does not advise technology users to select only those vendors with the highest ratings or other designation. Gartner research publications consist of the opinions of Gartner’s research organization and should not be construed as statements of fact. Gartner disclaims all warranties, express or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.

Enterprises need MSPs to meet their performance, productivity, security, and operational goals. MSPs bring in talented resources and tools that can reduce expenses and produce desired outcomes. They act as a catalyst to enhance the performance of IT infrastructures, especially with the proliferation of cloud and virtualization.
MSPs can be categorized based on the services they provide or the scope of their target customers and responsibilities. They can be Pure Play MSPs, Staffing Legacy MSPs, or High-level MSPs. They can also be categorized based on offered services like security management, managed IT support services, networking and infrastructure, communications, data analytics, and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
Investing in MSPs can help organizations overcome the shortages of skilled professionals, provide access to professional insights and expert resources, ensure business continuity, offer constant network monitoring, improve security, and manage costs effectively. This can lead to improved performance and customer experience.




